Why Try? The Impact of Screen Time?

Let’s face it. Parenting is hard. And frankly, things seem so much easier when our children are occupied with an iPad, phone, or similar device. Plus, they need skills for the digital world. And that’s how kids connect today, right?
So much pulls us toward more tech time for our children. But is this really what is best for their development? A study from August 2023 found that screen time for one-year-olds leads to developmental delays in communication and problem-solving when the children are aged two and four.
The impact continues as our children get older. Jonathan Haidt explains the high costs of a phone-based childhood in his book The Anxious Generation—How The Great Rewiring Of Childhood Is Causing An Epidemic Of Mental Illness. The first section of the book outlines the decline in teen mental health and well-being since the smartphone took over our lives. Haidt argues that this new technology, along with parental overprotection, has shifted our children’s lives from play-based experiences to an unprecedented state of fragmentation, disconnection, and even deprivation.
It’s interesting to hear children’s thoughts on this topic, too. When asked, kids are pretty self-aware of the impact screen time has on their lives. They speak about how they can be disconnected from others when they are on their devices and how getting outside actually helps them feel better. Young people also recognize that screen time can lead to crankiness, headaches, and even not-great sleep. They can identify “video game brain” and how hard it is to come out of that state. Young people are self-aware enough to notice how it’s easy to fall into an expectation that screen time will soothe a bad day but that in reality, it doesn’t and how taking a walk would be so much better.
Families whose children participated in Screen-Free Week from May 6 to 12 shared some lovely results. During that week, their children were kinder, better able to regulate their emotions, and more present in what they were doing. Children reported reading more, spending more time with their family, and reveling in being outside.
So what do we do? Our lives are so intertwined with technology that breaking already established habits can seem insurmountable.
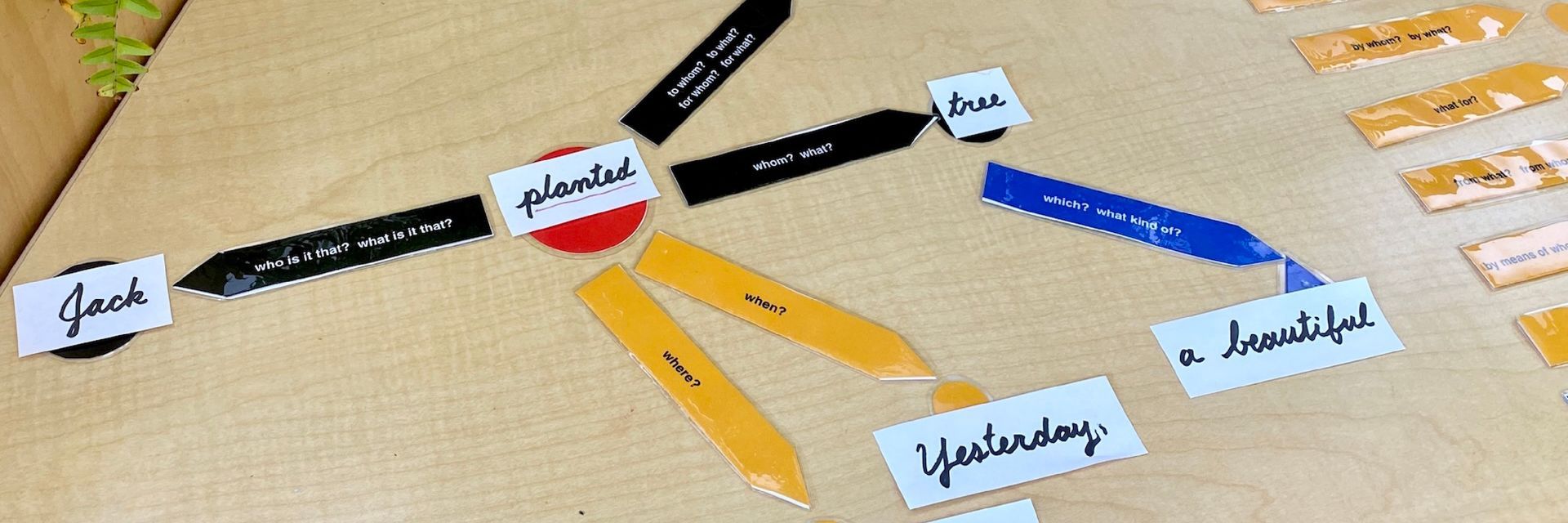
One first step is to be open with our children. For younger children, this can be as simple as setting limits and stating that things will be changing. Our little ones rely upon us to set the routine. They will test us, of course, because they need to know if we are going to hold true to a limit. But the process is pretty straightforward: decide to limit screen time and stick with the plan.
Our older children will appreciate some genuine conversation, which means also listening to their thoughts and concerns. When they feel heard and their opinions valued, young people can be pretty open to hearing adults’ perspectives. Through thoughtful conversation, we can explore options for reducing screen time. The next step is to try it out. Treat the process as a collaborative experiment, with the intent to come back together and discuss what worked and what was challenging.
If moving toward less screen time seems daunting, also remember that we can call upon our community! Make a commitment with other families and find ways to support each other. Publicly state your intent and goals. Share successes and challenges. Plan screen-free playdates and organize experience-based outings.
Our children deserve the best we can offer them during these crucial developmental periods of early childhood and adolescence. Yes, giving them an iPad or phone, letting them watch videos, or giving in to another online game can give us a little respite, but are these choices really serving our children well?
For additional support and resources, visit:
Please also feel free to contact us. At our school, we prioritize a play-based childhood and are happy to share more about what we do!