The Origins of Language

Dr. Maria Montessori felt that in order to support children’s development of language, we first need to appreciate the evolution of language. In fact, the language today’s children use is a culmination of language evolution from the dawn of humans.
Languages have expanded and grown to match the complexity of our cultures. Because language is changing and evolving, children create their language as it exists in their environment. Although a child born thousands of years ago had no less potential for developing language than a child today, our languages have grown in fullness and complexity.
Evolution of Spoken Language
Although we don’t have any records documenting the beginning of spoken language, we can imagine that certain experiences or events drove humans to produce different sounds. Over time these utterances likely became internalized and came to represent an experience.
Language is necessary for humans to work together cooperatively. In his memoir, Born a Crime: Stories from a South African Childhood, Trevor Noah relates his experience growing up in South Africa, where there are at least thirty-five indigenous languages, eleven of which are official languages. As someone who speaks seven different languages, Noah experienced first-hand how language can bridge divides: “Language, even more than color, defines who you are to people.”
Early humans developed language as a means of communication, but humans were isolated into small tribes or clans. Each group developed their own agreed upon communications. As populations increased and migration happened, communities came into contact. Some words got shared. Some new words were created. Etymology gives us the histories of the roots of words, and as such, historians can study the evolution of language and human migration through words and their roots.
The vocabulary of any language is related to the culture of that community. For instance, the Eskimo language has 27 different words for snow, while Hawaiians have no words for snow. Languages constantly evolve as new experiences emerge in our culture. Currently, we can see this in how words are added or removed from the dictionary. A couple of decades ago, for example, “Google” was not a verb!
Primitive spoken languages were primarily nouns interspersed with some adjectives, verbs, prepositions, and conjunctions. Primitive languages actually sounded a lot like how young children speak. As cultures evolved and became more complex, languages evolved their own vocabulary, grammar, and syntax.
Evolution of Written Language
At some point, humans also developed symbolic language as a way to record their thoughts. These records began as pictures, such as the cave paintings that date from over 30,000 years ago. In the beginning, the pictures were realistic and over time became more symbolic, moving from pictograph alphabets to phonetic alphabets. With a phonetic alphabet containing a limited number of symbols, people could begin to create any word. The birth of the alphabet greatly simplified the writing system. As civilizations evolved, expanded, and became more sophisticated, the expansion of language in written form became more universal.
The roots of modern American English reflect the diversity of the culture. While the English language originated in Britain, the Romans added a Latin influence and the French Saxons and Anglos added their own influences. As colonists came to America from different countries, they brought their language to a place where the Native Americans had their own languages. All of these influences were incorporated into American English.
This diverse history of the language is what makes it complicated and full of exceptions. Some words retained their original spelling while others were adapted and modified. This varied origin story explains why we can have a sound represented in so many different ways. Just think about the sound “sh” which can be represented in: shock, sugar, emotion, charade, social, and tissue.
Once humans developed a writing system as a way of recording thoughts, another skill had to be acquired — reading. If writing is recording our thoughts, reading is interpreting the thoughts of others.
Development of Language
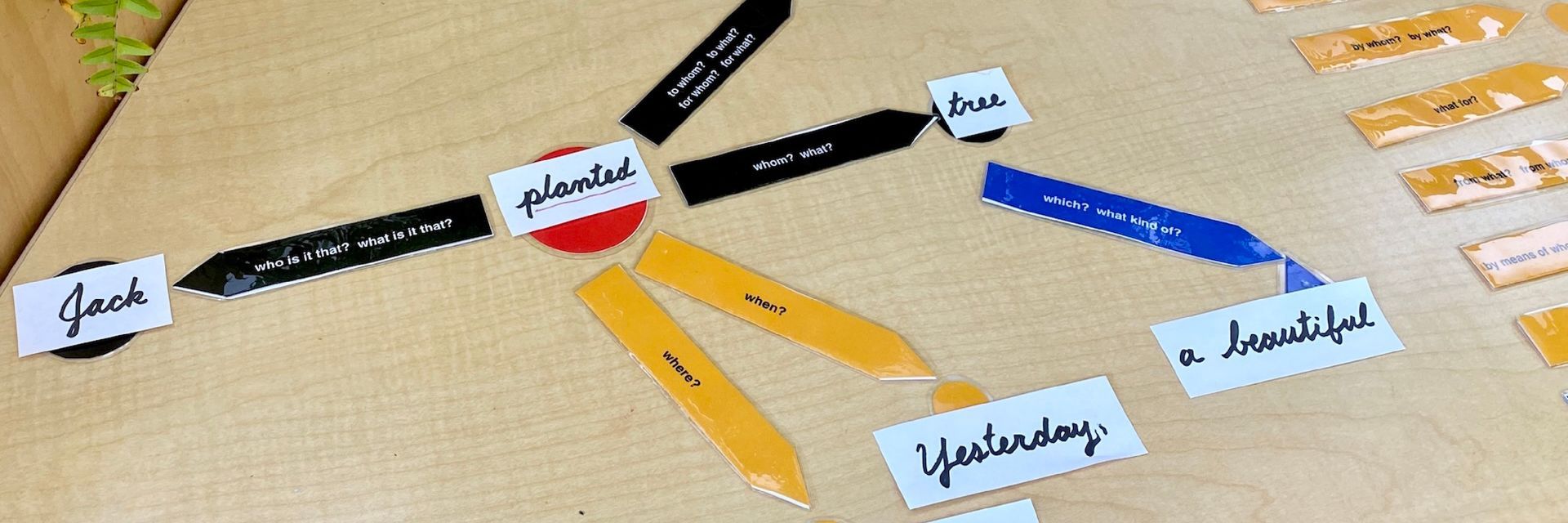
Just as the evolution of writing and reading happened with humans, there is just as much magic, mystery, and power that happens when each child learns to read. In our prepared environments, we offer children the keys to their language because we have a deep appreciation for the origins of language itself. By understanding the history of language, we can better appreciate what children are accomplishing when they acquire these skills.
Our exercises for language are not designed to teach language directly, but to offer support to children’s developing personalities. The method we use in our classrooms evolved from Dr. Montessori’s discoveries about how children learn. What resulted is a revolutionary method that is in harmony with the child’s developmental needs. Children can learn to write and read without even realizing that it is happening.
We welcome you to observe this development of language in action in our classrooms. Schedule a tour today!