The Impact of Grace and Courtesy
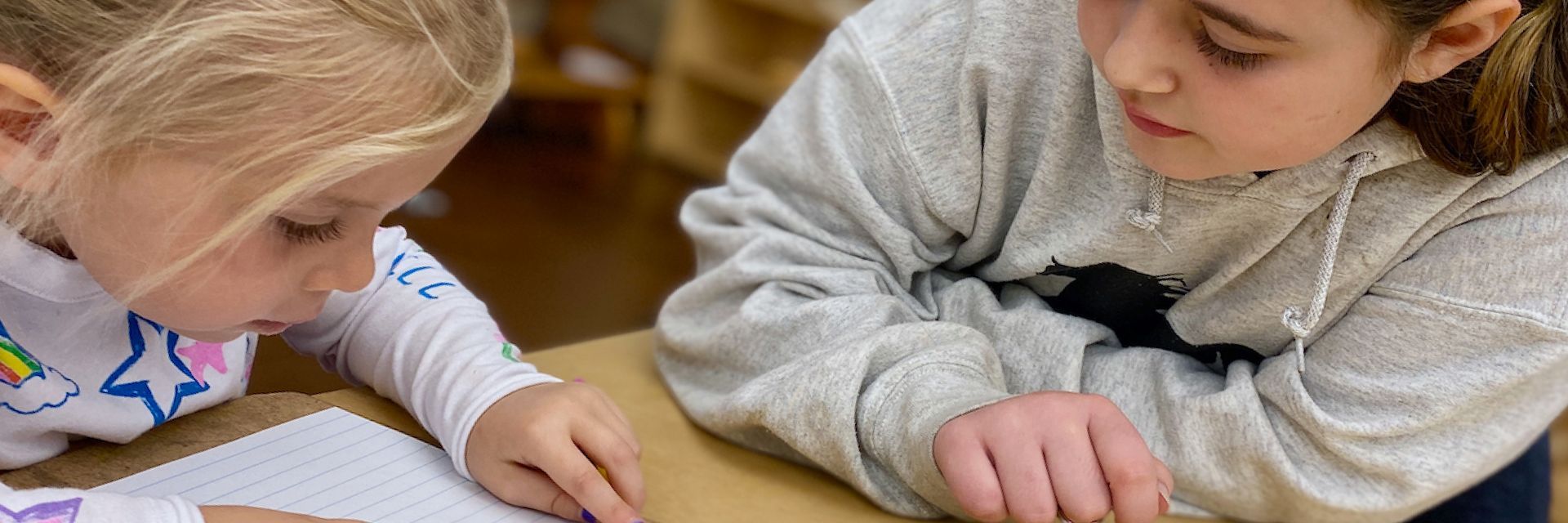

In Montessori, we emphasize two words on a pretty regular basis: grace and courtesy. But what does grace and courtesy really mean? How are they an essential part of Montessori classrooms? And what role do they play in supporting the development of social relationships?
What is Grace? What is Courtesy?
Let’s first isolate each word. Google’s Oxford Languages defines “grace" in two parts: 1. simple elegance or refinement of movement, and 2. courteous goodwill. Courtesy is defined simply as: the showing of politeness in one’s attitude and behavior toward others. Stated another way, grace and courtesy comprise how we move through the space around us showing respect for ourselves and others.
Grace & Courtesy Lessons
In our toddler and primary classrooms, grace and courtesy are considered to be part of practical life learning and we devote significant time to grace and courtesy lessons. For example, the adults give explicit instruction on how to walk around someone’s work on the rug, how to wait your turn, how to offer help, how to tuck a chair under the table, or how to introduce oneself. These lessons are offered one-on-one or in small groups and we often use role playing as a technique for exploring the skills.
We are very careful about how we introduce grace and courtesy to children. If we see something that needs to be addressed, we try to avoid confronting the child in the moment and we never offer grace and courtesy lessons as a form of punishment or correction. We are careful about this because children are often embarrassed when corrected by adults on the spot. When this happens, they can feel disrespected and not safe, and thus much less likely to perform the act on their own accord.
In the Older Years
As children enter their elementary and adolescent years, our approach shifts slightly. Elementary-age children are more focused on their social interactions and are learning how to navigate the ups and downs of friendships. As such, much of the grace and courtesy work at this level provides children with tools for communicating directly and respectfully, sharing perspectives thoughtfully, and even being discreet about something potentially embarrassing. In addition, they are learning how to interact with the broader community as they arrange visits or interviews, conduct themselves according to the norms of different communities, and explore how to be a host or be a guest.
The Goal
The goal in Montessori education is that these acts of grace and courtesy aren’t rigid expectations, like insisting that children say please and thank you. Rather, they become part of how children want to be and interact. Dr. Montessori is quoted as saying: “…the essential thing is that [the child] should know how to perform these actions of courtesy when his little heart prompts him to do so, as part of a social life which develops naturally from moment to moment.”
Like all other exercises in Montessori prepared environments, we offer opportunities to regularly practice and repeat grace and courtesy skills. Because these experiences are part of the normal functioning of the day, they provide a respectful way for young people to learn expectations and for adults to provide scaffolding and assistance for social skills.
The Results
In time, as we offer these grace and courtesy opportunities and give children a safe place to practice, our young people eventually perform these skills independently.
When you visit our school, you’re likely to see two young children sitting together one patiently showing the other how to tie their shoes. Or perhaps if you observe in a classroom, a couple of students might ask if you would like them to serve you tea or water.
Our children bring a sad classmate a tissue or rush to assist when someone has a spill. They tuck their chairs under tables so others don’t trip over them. They carefully place a tray upon a table. They greet each other and adults in the hallways. They hold the door open when they see someone coming their way.
In the process, Montessori children move beyond the basic niceties and think deeply about their impact on those around them. We’d love to show you this in action!
Schedule a tour to see the ways that grace and courtesy help children recognize themselves as caring individuals within a supportive community.