4 Montessori Quotes That Give Us Perspective
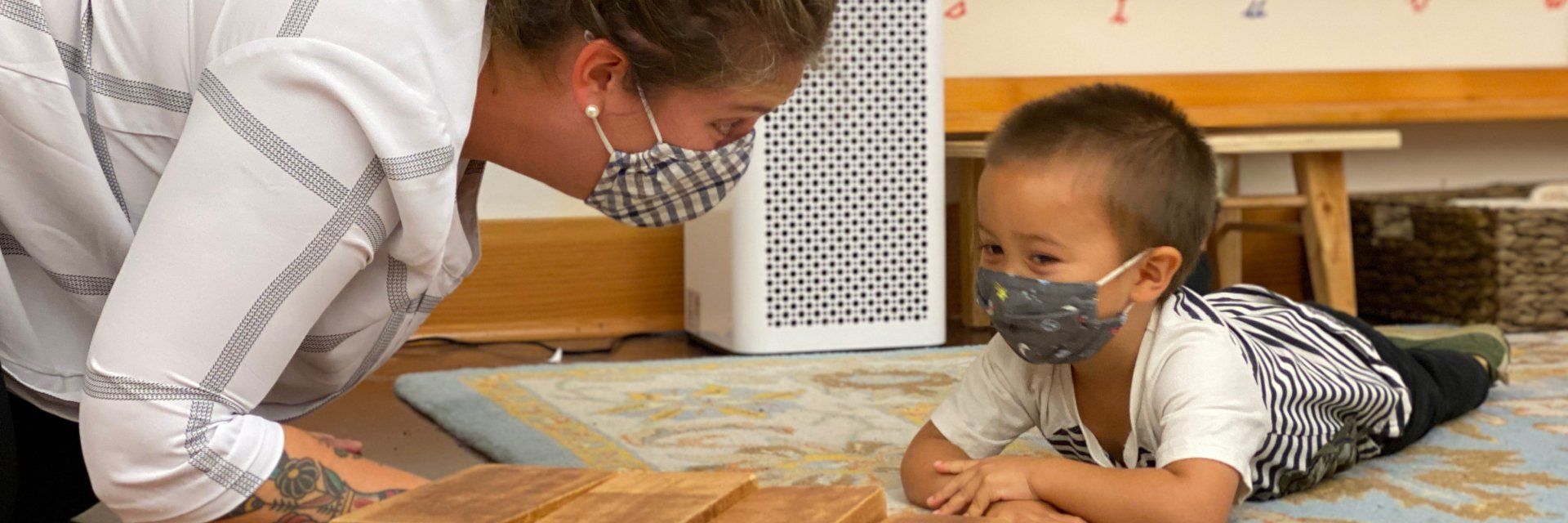

First and foremost, Dr. Maria Montessori was a scientist and physician. She stumbled her way into education when she observed the mistreatment of children put into her care. She recognized that adults (especially at the time) did not give children the credit and respect they deserved, and this launched her work that eventually became Montessori education.
Dr. Montessori was all of those things, but she was also a prolific writer and speaker. Her words have been translated into countless languages around the world and have been reread by innumerable people since they were written. A century later, the language can sometimes show its age, but it’s often beautiful, poetic, and inspiring. And that’s not to mention the brilliant ideas behind the words.
People love to quote Montessori, and for good reason. Here we share four excerpts from Dr. Montessori’s writing that we find particularly interesting, and thought you might, too!
“This is education, understood as a help to life; an education from birth, which feeds a peaceful revolution and unites all in a common aim, attracting them as to a single centre. Mothers, fathers, politicians: all must combine in their respect and help for this delicate work of formation, which the little child carries on in the depth of a profound psychological mystery, under the tutelage of an inner guide. This is the bright new hope for mankind.”
– Dr. Maria Montessori, The Absorbent Mind
Education is a profoundly important venture, on behalf of the individual as well as society as a whole. The way we choose to educate our children is perhaps the single greatest action we can take to pave the way for a better future for humanity.
And we can’t do it alone.
Education is a partnership. It takes well-trained instructors, inspirational leaders, participatory family members, and engaged communities to work alongside one another in support of the children. To know that all these parties can join together and work toward the common good is a pretty amazing concept, and incredibly powerful to see in action.
“An education capable of saving humanity is no small undertaking; it involves the spiritual development of man, the enhancement of his value as an individual, and the preparation of young people to understand the times in which they live.”
– Dr. Maria Montessori, Education and Peace
Individuality and flexibility are two critical components of any successful education. Human beings are not photocopies and we cannot treat them as such. To develop a curriculum that is delivered unwaveringly to a diverse group of children without any deviation from the predetermined path does not serve the child.
To employ an educational process that supports the individual development of the child not only honors their own unique path, but it stands to be timeless. Human development, with all its variations, remains fairly similar throughout the generations. Even as the world changes around us, and we look toward an unpredictable future, Montessori education prepares children for what lies ahead.
We teach children to ask their own questions and seek their own answers. We guide children to listen to their inner passions. We explicitly show children how to interact with other people around them so that they may honor individuality while working cooperatively. To do these things is to prepare children for anything.
"The mind takes some time to develop interest, to be set in motion, to get warmed up into a subject, to attain a state of profitable work. If at this time there is interruption, not only is a period of profitable work lost, but the interruption, produces an unpleasant sensation which is identical to fatigue.
Fatigue also is caused by work unsuitable to the individual. Suitable work reduces fatigue on account of the pleasure derived from the work itself. Thus the two causes of fatigue are unsuitable work and premature interruption of work."
– Dr. Maria Montessori, What You Should Know About Your Child
Adults traditionally have a habit of inserting themselves too frequently into the work of the child. We feel duty-bound to teach and to guide, when in reality it’s our job to clear the path and stand back while they take the journey themselves. Getting in the way is rarely done with ill intent; it’s simply what we learned when we were children. We want to be helpful. And it can take a lot of unlearning to allow our children to truly learn for themselves.
There is a very delicate balance, and it takes a lot of observation to get things right. We learn to sit back, notice what the child is doing, take a pause, and notice some more. We fight the urge to jump in and correct things for them, for those are precisely the moments when learning happens. If a child is allowed to make mistakes and then to fix those mistakes, they gain not only skill knowledge, but the confidence to repeat the process in the future.
That’s not to say we should never step in. The careful observation we mentioned also helps adults ensure that a child is not faced with a challenge they are not yet prepared to face alone. The key is to understand basic child development while simultaneously paying close attention to the individual’s needs.
“To let the child do as he likes when he has not yet developed any powers of control, is to betray the idea of freedom ... Real freedom, instead, is a consequence of development; it is the development of latent guides, aided by education.”
– Dr. Maria Montessori, The Absorbent Mind
Taking the last point a step further, Montessori educators and parents need to understand what freedom with limits really means.
Should a child be permitted to eat candy for breakfast every day? Should they be expected to eat every meal that is placed before them without opinion? No, on both counts. What lies in the middle can vary from time to time, but perhaps the child is allowed to serve themselves an amount they know they can eat, or perhaps they get to have a say in what they would like to eat some of the time. The same principle can (and should) be applied to almost everything.
We must give children limited, developmentally appropriate choices.
As they gain new skills, we give new choices. It’s an ever-evolving dance between choice and structure, and it’s one of the most important things we can do for our children.
____
Hopefully we’ve sent a little inspiration your way. Want to read more? Let us know and we can recommend (and maybe even lend) some great books.

Contact Us
© 2024 The Montessori School of the Berkshires
PO Box 422, 21 Patterson Road, Lenox Dale, MA 01242