Materials Spotlight: Racks and Tubes

Racks and Tubes, The Test Tubes. They may go by different names, but they’re all the same: a gloriously detailed Montessori division material. Introduced to the child any time between the end of their Children’s House experience or even in the older elementary years, the tiny parts of the material are beautiful and appealing. Adults who have had an opportunity to see the Racks and Tubes used are usually delighted by the way this physical material is able to help children understand more deeply how numbers are manipulated during division.
This is something so much more than when we learned long division with paper and pencil. Of course, that is taught simultaneously, but having the material can help everything make more sense.
The Material
A whole lot more complicated than math materials the child has previously used, there are many components, including:
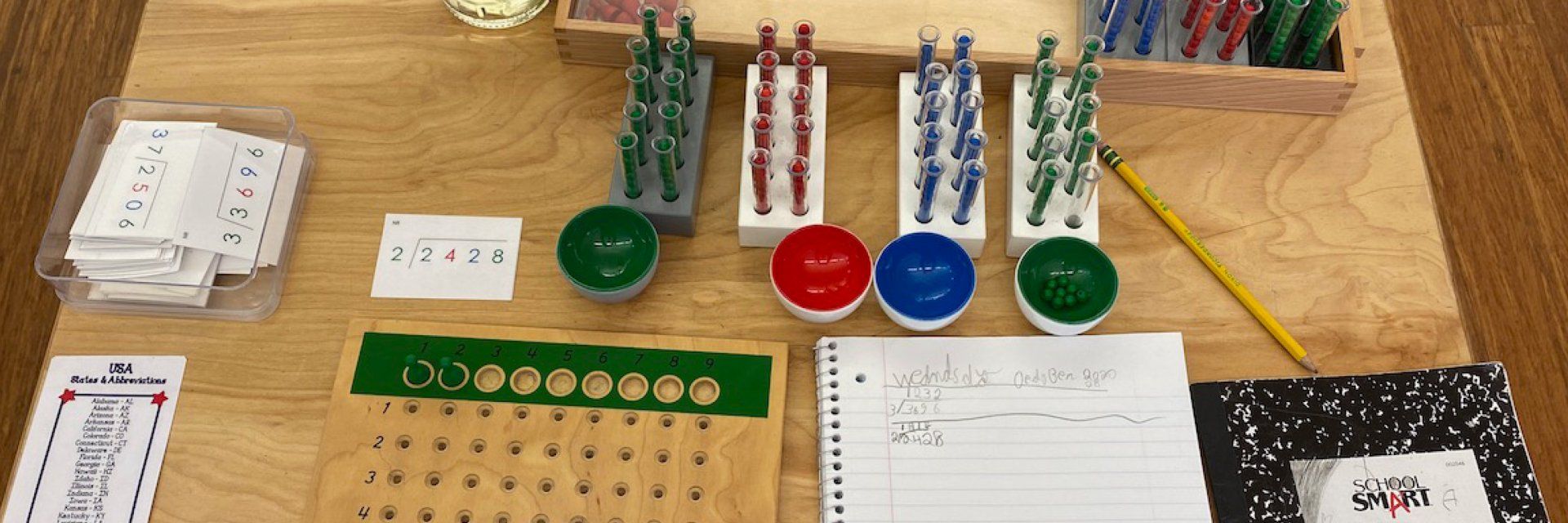
- Seven test tube racks: Three of the racks are white and the tubes in each contain green beads (units/ones), while another has tubes filled with blue beads (tens), and the last is filled with red beads (hundreds). This pattern is repeated with three gray racks and tubes filled with beads (thousands, ten thousands, hundred thousands). The final rack is black, and its green beads represent millions.
- Seven bowls with external colors to match the racks and internal colors to match the beads.
- Three wooden frames, each with 81 holes in which beads may be placed.
The color scheme of green, blue, and red being representative of units, tens, and hundreds is repeated throughout many Montessori materials. The child will have already seen this when using the stamp game, bead frame, and checkerboard materials.
Setting Up
As an example, we will refer to the division problem 9,764/4=2,441. We begin by laying out the green board. The other boards will not be used for this problem, because the divisor (4) is only one digit. Larger problems require more boards (more on that later).
To represent the divisor, we will take out four green skittles and set them into place at the top of the board.
The first four racks are all we will need for this problem, so we will take those out along with their corresponding cups.
To make 9,764 we place the correct amount of beads in the appropriate cups: 4 unit beads in the unit cup, 6 ten beads in the ten cup, 7 hundred beads in the hundred cup, and 9 thousand beads in the thousand cup. The cups are then lined up neatly above the board.
Often at this stage in their mathematical development, students are recording their work on paper, so you would notice the child writing the problem down and filling in the answer as they go.
One Divisor
To begin solving the problem, it’s all about even and fair distribution. Starting with the thousand cup, beads will be placed beneath each skittle, one at a time, until all the beads are used up. The only catch is, the distribution cannot have any remainders (until we get to the last step with the units). This means that beneath each of the four skittles there will be two beads, with one left over.
By now, the child will be fairly proficient in exchanging across place values. They will know that one thousand is equal to ten hundreds, so the lone thousand bead will go back in its tube and ten red hundred beads will be put in the hundred cup.
The distribution continues with the hundred beads. After careful placement of each bead, there will be four underneath each skittle, with one leftover. This one hundred bead will be exchanged for 10 ten beads. This means there will now be 16 blue ten beads in the cup, which distributes evenly. The last step leads the child to distribute just four green unit beads, with one under each skittle.
The answer to a division problem is always what is found in one of the equal and fair groups, or what the child can count up underneath one of the skittles. The answer is always what “one” gets. In this case: 2 thousands, 4 hundreds, 4 thousands, and 1 unit, giving them the answer 2,441.
Long Division
When it comes to long division and completing more complicated problems with larger divisors, the racks and tubes are both elegantly and downright complicated. Reading a step-by-step description is not nearly as exciting (or clarifying) as seeing one completed in person. We strongly encourage you to observe this material being used in our elementary environment when you’re able.
In the meantime, we can give you the gist. Let’s say we are dividing 71,326 by 304. We would lay out the green, blue, and red boards (because there is a three-digit divisor). Three skittles would be placed at the top of the hundred board, zero would be placed on the ten board, and four would be placed on the unit board.
Beads to correspond with 71,326 would be distributed into their corresponding cups.
To begin distribution, the ten thousand cup would be placed above the hundred board, the thousand cup above the ten board, and the hundred cup above the unit board. One at a time, beads would be distributed across the skittles on all three boards. The student stops when they can no longer continue fair and even distribution.
Here, the child would pause and note how many hundred beads are beneath one of the unit skittles. This number is recorded on their paper, as it is part of the final answer.
The problem continues with cups sliding to new spots and beads being exchanged as needed. The distribution continues until the problem is complete.
This may all sound horribly tedious to an adult reading about it, but we can promise you it’s absolutely thrilling to the child who is discovering these number processes for the first time. We can also reiterate the fact that by using their hand to manipulate physical materials, the child is giving their brain visual scaffolding in which to solidify their understanding of division.
As we mentioned above, the very best way to see the magic of this special material is to watch it being used in person. We know that’s not always possible, but when you do have an opportunity we think you’ll be just as amazed as we were the first time we saw it.
Questions? Want to learn more about the Montessori approach to math? Contact us any time. We love to chat about our methods!