Grasping the World: Geography for Young Children

Between mass media and family travel, young children are exposed to all sorts of language about their planet. They may hear phrases like “going around the world,” “as the world turns,” or “the other side of the world.” Young children absorb this information yet still need concrete experiences to help make sense of what “the world” even means!
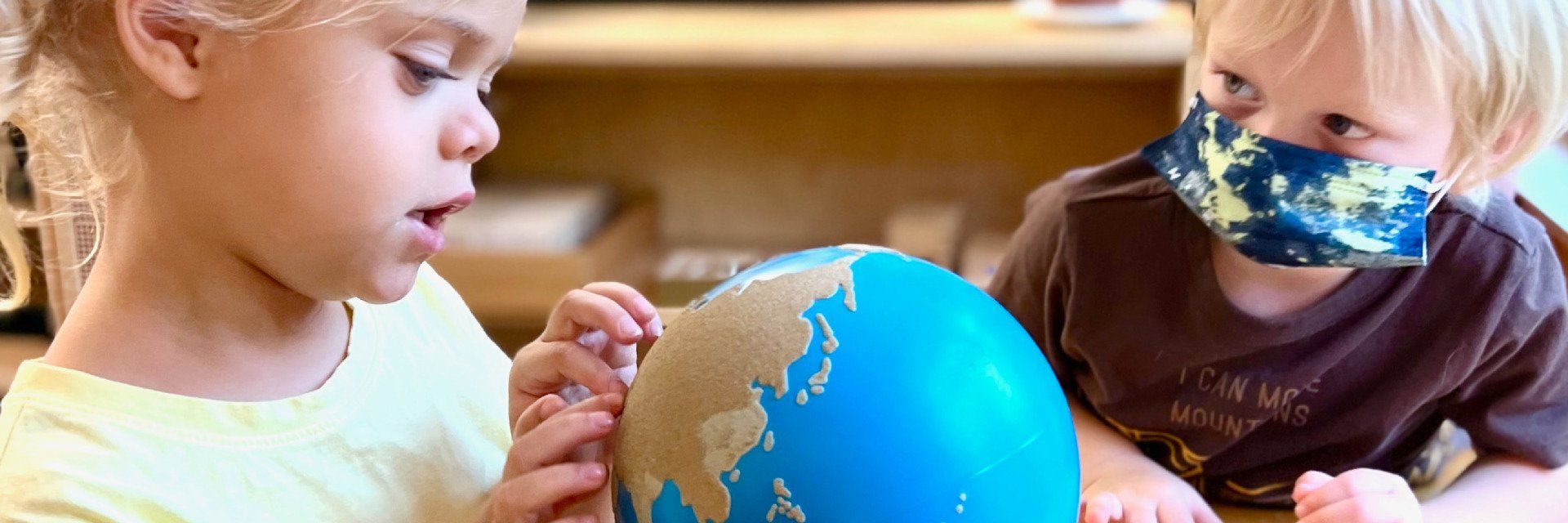
Over 100 years ago, Dr. Maria Montessori observed how younger children were drawn to the globes that older children were using. Through careful observation, Dr. Montessori came to understand how young children crave a concrete understanding of concepts like the world, the earth, and the globe.
Concrete Materials
In Montessori, we offer concrete materials so children can experience accurate representations of these abstract concepts. We start by providing a small globe. The land surfaces are covered with fine sandpaper and the water surfaces are covered with smooth blue paint, so children can tactically explore the distribution of land and water surfaces over planet earth. With the globe, children get to literally grasp the shape of the planet and have a richer understanding of phrases like “going around the world.”
We also have a set of materials so children can learn about different kinds of land and water forms. Children can pour water into beautifully created models of an island, lake, peninsula, gulf, isthmus, strait, cape, bay, archipelago, or system of lakes. The water flows into the water area (painted blue) and moves around the land area (painted brown). As children learn the names of these land and water forms, they also explore folders with photographs of actual land and water forms from around the world.
Montessori classrooms also have a second globe to show how the land surfaces are divided into continents. Each continent is painted a different color (green for Africa, red for Europe, orange for North America, pink for South America, brown for Oceania, and white for Antarctica). The color coding of the continents stays consistent throughout all the materials, which helps with association and retention.
Once children have grasped this concept of the land and water distinctions on the globe, we show them a flat puzzle map divided by the Eastern and Western hemispheres with each continent (color-coded as above) as a separate puzzle piece. This continent puzzle map gives children the chance to see all of the continents at once as they look on a two-dimensional map.
We also offer maps of each continent to show the political partitions formed by countries. Each puzzle piece is a country, with the knob for picking up the piece located at the country’s capital. Children initially use these puzzle maps in a very sensorial way, taking the maps apart and putting them back together. As children engage with this experience, we begin introducing the names of the continents and then the countries. Young children absorb this vocabulary effortlessly and delight in learning the names of all the countries. As children get older, they also enjoy taking on additional challenges, sometimes even closing their eyes, feeling all the way around the puzzle piece, and then naming the country!
Cultivating Appreciation
Although this is all rather impressive, it’s important to remember that our purpose is not to turn children into walking encyclopedias. Even when children may come to rather astonishing intellectual skills, these abilities are a by-product. Our purpose is to offer young children activities to help them understand their place in the world, become aware of the oneness of humanity, and appreciate the incredible variation among people that results from physical geography and humans’ creative efforts and inventions.
To help in this effort, we share collections of pictures of human life organized by continent. These pictures offer impressions of different modern cultures, lifestyles, and traditions. The pictures reflect commonalities of human needs and the great variety of ways humans fulfill these needs. The photographs highlight regional food, farming, shelter, transportation, daily life, traditions, and the physical geography represented in landmarks, climate, flora, and fauna.
As children develop a relationship with the world around them, they may also explore more about the different places in the world, including climates, plants, and animals. Often children love to begin creating their own maps by carefully tracing the puzzle map pieces and coloring and labeling the continents and countries.
In Montessori education, children absorb a great deal of geography skill knowledge! But our focus is on giving children the opportunity to develop a constructive and creative relationship with the whole world, as well as a love for how our planet offers a diverse home to the whole of humanity.
Schedule a tour to see this love of geography in action!

Contact Us
© 2024 The Montessori School of the Berkshires
PO Box 422, 21 Patterson Road, Lenox Dale, MA 01242