Developing Fine Motor Skills

Developing fine motor skills is critical for everyday activities. There are many ways to help children along this process, and Montessori classrooms have specifically designed materials that are intended to strengthen the small muscles in hands and wrists. The strengthening of these muscles allows us to make more precise movements and perform detailed tasks, as opposed to the large muscles required for gross motor activities like jumping and walking.
While fine motor development is supported at various levels in Montessori environments, we can observe the bulk of this work occurring during the primary years, when a child is between the ages of three and six. Three areas of the classroom play particularly important roles: sensorial, practical life, and language work. In this article we highlight some of the ways Montessori materials in these areas help children strengthen their hand and wrist muscles. Interestingly, these materials have other purposes as well, thereby teaching a wide range of skills.
Sensorial Materials
● The Pink Tower
A series of pink cubes are meant to be stacked vertically from largest to smallest, with the top block measuring 1cm cubed. Using this material requires a child to use their focus and carefully balance each block, using precise movements as the blocks get smaller.
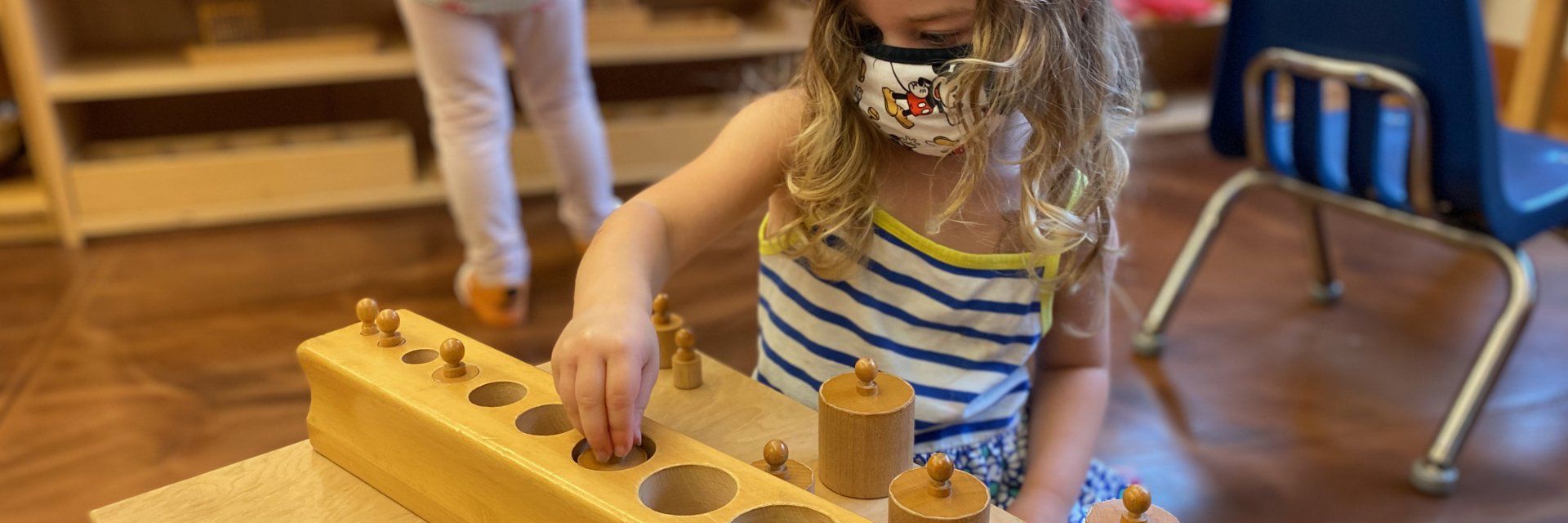
● Knobbed Cylinders
Wooden cylinders of varying sizes fit into a block designed for this purpose. Each cylinder has a tiny knob for children to hold onto, and there is only one way to fit the cylinders correctly. In addition to developing fine motor skills and their pincer grip, this is one of many materials that aid in developing visual discrimination.
● Mystery Bags
A small cloth bag containing tiny objects and miniatures, a child is meant to feel inside, hold the objects, and determine what they are without seeing them.
Practical Life Materials
● Clothespins
Montessori students learn to wash clothes or linens used in the classroom. One step in the process is, of course, hanging the cloth to dry using clothespins.
● Spray Bottles
Spray bottles are used for a variety of practical life activities in the classroom, including window washing and plant care. The repeated action of squeezing the trigger on the bottle is great for strengthening hand muscles.
● Crumbers and Dustpans/Brushes
Again, with a focus on precision and careful use, there are several practical life materials used for cleaning up the classroom that are also fantastic fine motor tools. Dustpans and brushes are used for cleaning up messes on the floor, while crumbers are similar sets meant for picking up on the surface of a table after eating but before washing the table.
● Cooking Utensils
A major part of Montessori practical life work is food preparation. There are countless kitchen tools that are used in this learning, and so many of them require the development of fine motor skills. Just a few of these include: vegetable peelers, knives for chopping, apple slicers, whisks, and spatulas.
● Dressing Frames
One of the most direct fine motor materials, the dressing frames teach children to fasten clothing in a variety of ways. A wood frame with two cloth panels is attached in the center. Children practice lacing, buttoning, buckling, snapping, zipping, pinning, and more.
Language
● Sandpaper Letters
Perhaps one of the most famous Montessori materials, the sandpaper letters are small wooden tiles with textured letters in the surface. In this preparation for handwriting and reading, children use their index finger to trace the shape of the letter while saying the sound it makes aloud.
● Moveable Alphabet
When learning how to write, children are ready to share their ideas before they are ready to grip a pencil. The moveable alphabet is a set of tiny wooden letters that children lay out on a work rug to spell words, phrases, and sentences. Organizing these small letters takes plenty of hand control.
● Metal Insets
Another material that is meant to indirectly prepare the child for handwriting, the metal insets are like a stencil that children use colored pencils to trace, create lined patterns within, and follow a series of directions to recreate the shapes on paper. This is often a child’s first real experience with learning how to hold a pencil properly, and aids in developing the critical pincer grasp. Some Montessori environments even provide triangle-shaped pencils to aid in this process.
Bonus: Pin Punch
A small wooden or plastic stylus with a sharp metal tip is used to make perforations. Children will often trace a shape onto a piece of construction paper, place the paper onto a specific soft surface, and use the pin punch tool to make a series of holes along the drawn line. If they take their time and do this correctly, they are able to punch out their shape upon completion.
Want to learn more? Curious to discover ways you can support your child’s fine motor growth at home? We welcome questions and love to talk about children’s development. Contact us today for more information.

Contact Us
© 2024 The Montessori School of the Berkshires
PO Box 422, 21 Patterson Road, Lenox Dale, MA 01242