Montessori at Home: Caring for Pets Montessori-Style
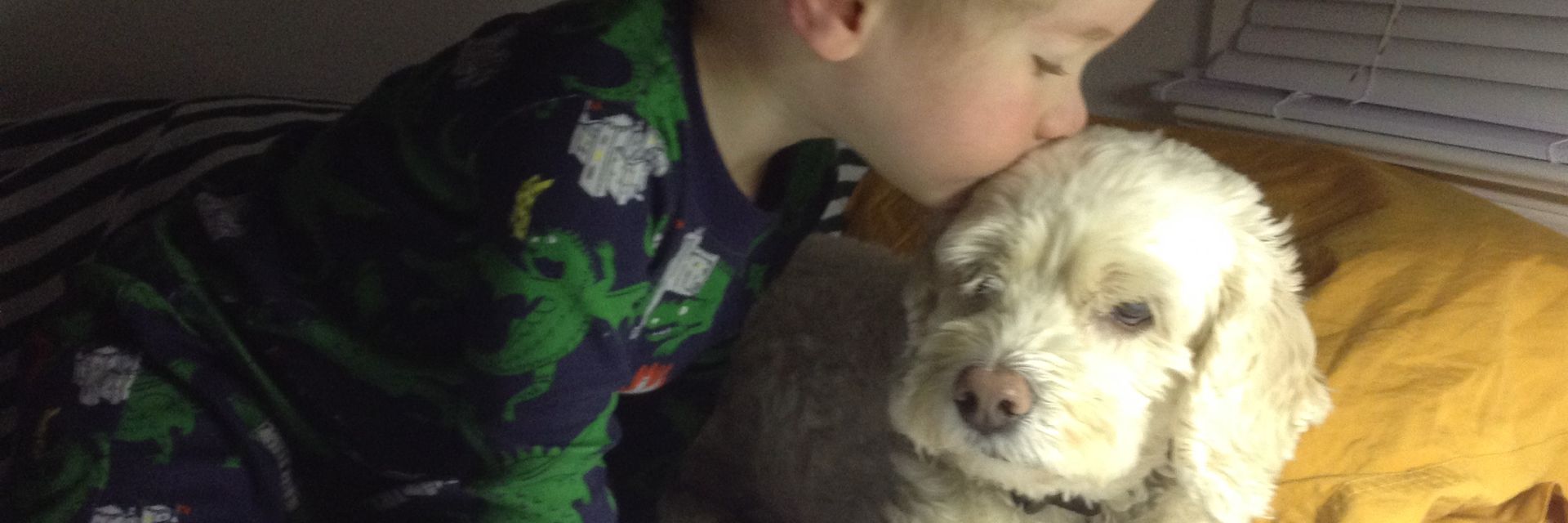

The summer months can be a wonderful time to integrate some Montessori principles and practice into our home environments. With that in mind, our focus this week is on how to care for pets, Montessori-style.
Montessori classrooms regularly have pets as part of the community for a number of reasons. When children have contact with the natural world, especially when they are part of taking care of living things, they develop a deep reverence for life in all its forms. In addition, as children are learning how to independently care for themselves, they can apply their skills to caring for an animal, leading to increased self-control and responsibility. Becoming aware of and attuned to another being’s needs supports the development of increased empathy and compassion.
“Children have an anxious concern for living beings, and therefore the satisfaction of this instinct fills them with delight. It is therefore easy to interest them in taking care of plants and especially of animals. Nothing awakens foresight in a small child, who lives as a rule for the passing moment and without care for the morrow, so much as this.”
– Dr. Maria Montessori, The Discovery of the Child
Daily Care
If you already have a pet or pets at home, encouraging children’s participation in their daily care is a good place to start. The easiest first step is giving a pet food and water. Even young toddlers can do this! The key is having the correct amount of food prepared in an easy-to-dispense container. The container can be placed on a tray or consistent place that is available for your child to access, carry to the pet’s food bowl or space, and then pour or place for the pet.
If the pet is a fish, a small dish for the food can work. A hermit crab might need a small piece of fruit stored in a container that can be easily opened so the fruit can be retrieved and placed into the habitat. Whereas a larger animal like a dog or cat, will likely need a portion of food in a container that can be poured into their food dish, or, in the case of wet food, scooped out and transferred to the food dish.
The same approach can be applied to refilling a water bottle for hamsters or gerbils or pouring water into a water dish for larger pets. Ensure your child can access the water source and has a child-sized pitcher or measuring cup that holds just the right amount of water for your pet.
Break it Down
To make the process most successful, it’s best to think about breaking down the steps and making sure the materials are accessible and child-friendly. Does the container open easily? When pouring does the food or water come out from one place so it goes where intended? How far is the reach to get food into a habitat? Look at everything from your child’s perspective and anticipate any obstacles.
After figuring out the best materials and set-up, the next step is to show your child how to complete each part of the process. For young children, always make sure there are a limited number of steps. It can help to have a visual guide available, too. For example, if the pet needs to be fed once in the morning and once at night, you can have a picture that represents this. The visual guide can be laminated or put in a sheet protector and hung at your child’s eye level. Older children can use a dry-erase marker to check off when they have fed the pet.
Cleaning or Grooming
The same practice can be applied to other parts of pet care. Perhaps the food area needs to be cleaned by washing the dishes, wiping a mat wiped, or sweeping spilled food. The learning process can be incremental. In the beginning, maybe your child is just misting something like a hermit crab habitat but over time learns how to clean the enclosure, too. Other animals might need their bedding replaced or washed. If a pet needs a bath, a young child can be part of filling the tub with water or scooping water for rinsing. Eventually, children can take ownership of more and more of the process. If your child is ready for more responsibility, they can also learn how to independently clean or groom your pet. From brushing to bathing, children can be involved in various aspects of pet care!
Interacting & Playing
Learning how to interact with pets offers children opportunities to learn how to read non-verbal cues and anticipate needs. In treating animals with care, children get to practice grace and courtesy which helps them extend these skills throughout all their relationships. We all appreciate gentle touches, soft approaches, and respectful care!
Different pets require different kinds of toys and handling. Children can be involved in creating some play items for particular pets, such as toys on a string for cats to chase or making a yarn pull for birds. Children can get creative with finding things around the house for a pet to use, like recycling toilet paper rolls for gerbils to chew. Older children can research healthy treats or training tips.
Children can take on other responsibilities, too, such as taking a dog for a walk or being involved in training. Even small animals can often experience different levels of training, such as parakeets learning how to make certain sounds or to perch on a finger. Having books and resources available for children to learn more about their pets is another nice extension and cultivates more curiosity about what living things need and how to provide for them.
Ultimately, children like to be involved in the care of their pets. It is important for them to feel the connection with their beloved animals, and foster the feelings of responsibility and self-confidence that come with it.
If you would like some inspiration for how to support your child’s care of pets, let us know! We are happy to share our experience with having pets in our classrooms.

Contact Us
© 2024 The Montessori School of the Berkshires
PO Box 422, 21 Patterson Road, Lenox Dale, MA 01242